There is very good evidence accumulating that the use of therapeutic vibration will enhance and accelerate healing while having no adverse affects. In this guide we will discuss the evidence and practical applications.

There is very good evidence accumulating that the use of therapeutic vibration will enhance and accelerate healing while having no adverse affects. In this guide we will discuss the evidence and practical applications.
There are several types of evidence supporting the use of vibration to improve and accelerate healing.
Therapeutic vibrations have been proven to increase circulation, which will increase oxygenation and the nutrient supply to healing tissues. For more info: The scientifically proven effects of vibration massage- with clinical applications
Therapeutic vibrations have been shown to decrease post exercise soreness and speed the recovery of full function. Soreness and reduced function are the result of strenuous exercise causing microscopic damage to the muscle fibres. It is assumed that the reduced soreness and improved function result from that damage healing. For more info: The best massage for sports recovery
Several clinical trials have found that therapeutic vibration speeds and improves healing in patients suffering from diabetes (1–3). The researchers believe that this is due to the vibrations improving circulation. A review of the studies (3) concluded:
“This scoping review summarized the evidence regarding the effectiveness of vibration therapy for hard-to-heal wounds. Low-frequency and low-intensity local vibration therapy is useful for promoting wound healing based on evidence from human studies. The current optimal settings could be summarized as follows: local vibration at a low frequency within 47Hz and low-intensity (1.78 m/s2) for less than 30 min, three times a day, and five weeks.”
Studies performed on animals (rats and mice) show improvements in healing far more profound than just due to increased circulation. These are detailed in the appendix below, but include:
Researchers are unable to test whether similar things occur in humans because they cannot deliberately injure large numbers of people then later dissect them to examine the results. As long as it is safe though it is perfectly reasonable to assume that the results apply to humans. As an example, vibration is often used to speed and improve fracture healing. This was adopted following research which was done by breaking bones in sheep.
The researchers investigating diabetic patients strongly recommend the use of therapeutic vibrations to help healing, stating that it is very effective and has no adverse effects. Therapeutic vibrations have also proved to be very effective for reducing post exercise soreness and speeding the recovery of function. However, the potential uses and benefits may extend to any situation where healing is required.
While the diabetes researchers state that there are no adverse effects, one would need to use some sensible clinical judgment in other circumstances such as applying the vibration away from injured tissues until they were structurally sound enough.
The research suggests that if you use therapeutic vibration in the 40-50 Hz range as therapy for any musculoskeletal condition you will help speed and improve healing. However, the diabetes and animal research showed that good results were obtained by using repeated applications over time.
This could be used in any case where healing is involved, whether it is strained muscle through to something more complex. With appropriate advice patients can easily self apply 40-50 Hz therapeutic vibration using one of our massagers.
As discussed in our guide The guide to evidence based percussion massage (massage gun) usage , massage guns (percussion massagers) are designed to drive their heads in like jackhammers rather than send in therapeutic vibrations. Because of this:
Healing bone fractures
Wound healing
Muscle injury
Blood vessels
Increased levels of growth hormones
Nerve tissue
The results in the scientists own words
References
There have been a large number of trials investigating the effect of vibration on the healing of bone fractures. All trials showed that the application of vibrations sped up healing remarkably (1–9). Therapeutic applications have generally been in the range of 35-45Hz, with applications of 20-30 minutes per day. Researchers have viewed healing on xrays, measured various blood chemical levels and noted the number of osteoblasts (bone producing cells).
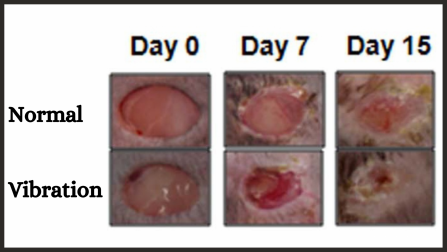
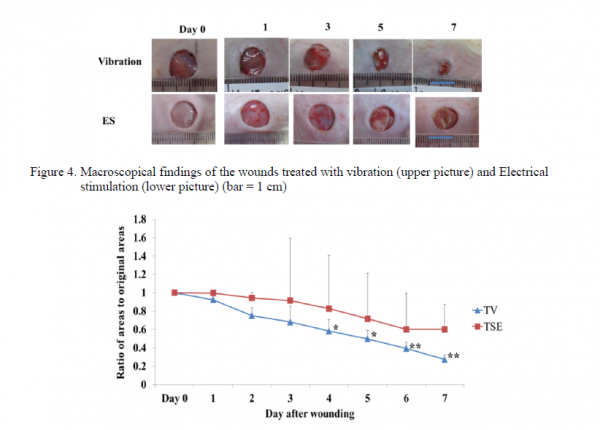
We found two trials that measured the effect of vibrations on wound healing. The results are illustrated in the following pictures.
Trial (13): This photo and graph shows the effect of applying 45 Hz vibration for 10 minutes per day, as compared with using an alternative method of stimulating growth: electrostimulation.
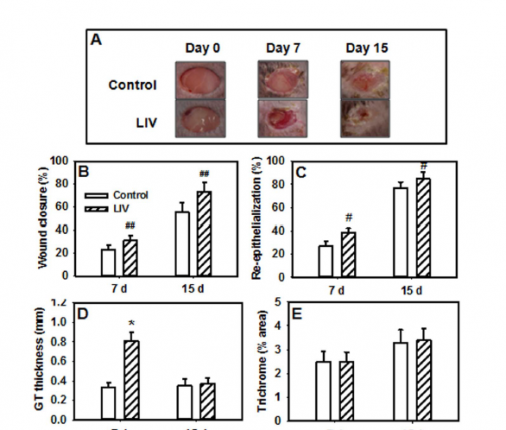
Trial (14): This trial used 45 Hz for 30 minutes per day. LIV stands for low intensity vibration, while the controls were allowed to heal naturally.
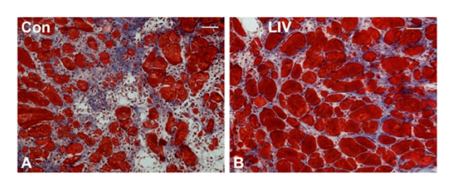
A study into the effect of vibration on the healing of muscles used applications of 45 Hz for 30 minutes a day. As shown in the following pictures this resulted in a remarkable:
This photo shows the effect on healing muscle of 45 Hz vibration for 30 minutes per day. It shows muscle fibres in cross section. Those receiving vibration have clearly grown much larger (15).
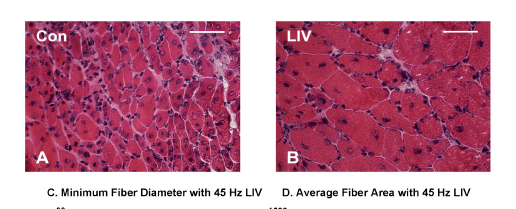
From the same trial. In these photos the lighter staining represents fibrous scar like tissue, while the red is the muscle fibres. This clearly shows that the application of 45 Hz vibration for 30 minutes per day resulted in healing and muscle growth with far less scar tissue. Scar tissue is detremental because it reduces flexibility and has no functional strength.
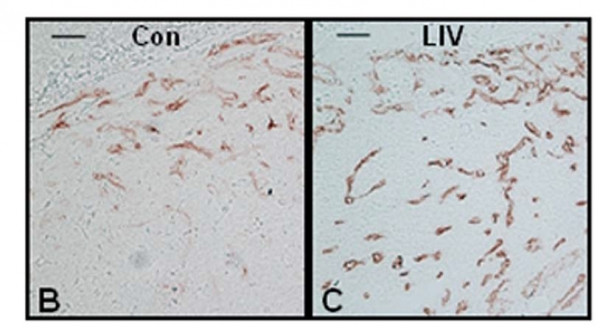
The formation of blood vessels is very important as it allows nutrients to be delivered to the healing tissues. In these pictures the darker lines are the blood vessels. It shows that vibration (LIV) cause the growth of a lot more blood vessels (14).
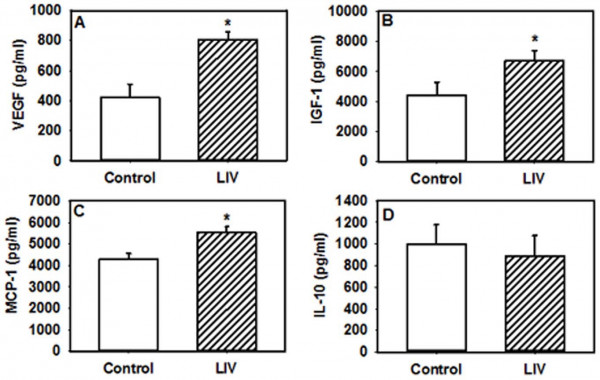
Growth hormones are your body's natural version of the steroids body builders and athletes illegally use. Of course these are legal and enhance your body rather than cause long term harm. As shown in these graphs vibration of 45 Hz for 30 minutes a day caused a remarkable increase in several of these (14). Where the graph shows a lower level it's actually a good thing for that chemical.
Scientist investigating the effect of vibration on the healing of nervous tissue by deliberately injuring the brachial plexus on a large number of mice (13) . What the found was truly remarkable. We’ve reproduced their summary of findings in an appendix, but in summary the vibration was found to:
The following is a direct quote from the trial testing the effects of vibration on the healing of injured nerves. There are a few technical terms, but overall it's pretty easy to understand (13).
Mechanical vibration massage treatment has obvious effect on muscular atrophy induced by nerve root injury. It can dilate capillary, increase volume of blood flow, so as to greatly improve blood supply and nutrition in local tissue; It can make the wall of micrangium rhythmically flatten and restore, accelerating flow of blood; And it can promote contraction and extension of muscle fibers, strengthen muscular tension, elasticity and tolerance, so, it can prevent and cure muscular atrophy.
Benign stimulation of mechanical vibration massage can activate the response of nerve immune and neuroendocrine systems, and transmit the signals to the submandibular gland through complicated ways, promoting secretion and storage of NGF in the submandibular gland. Finally, NGF is transported to brachial plexus root injury area through digestive, circulative and nerve systems.
Mechanical vibration massage can effectively promote the repair of myelin sheath and axes of injured brachial plexus in the rat. It can effectively improve blood circulation of the injured myelin sheath, promote proliferation of SC and survival of the cell body of injured neurons, so as to form a necessary regenerative micro-environment early for repair of nerve, and it induces stress responses of immune and neuroendocrine systems in the rat,promotes secretion of NGF in this gland, and it can improve peripheral nerve units and excite peripheral nerves, so as to accelerate their conduction reflection.
Na+, K+-ATPase activity on the surface of muscular cell membrane is an important limited factor for excitability and contractile strength of muscular cells. After skeletal muscles lose nervous innervation, generation of ATP is hindered, so Na+, K+-ATPase activity decreases. Under the mechanical massage stimulation, the muscular cells cultured in vitro show increases in stress-related gene expression and protein synthesis, leading to adaptability reconstruction of structures and contractile characters of the muscular cells, which are closely related with activation of Na+, K+-ATPase, and influences the distribution and functional activity of Na+, K+- ATPase on the surface of muscular cell membrane. In brief, mechanical vibration massage can promote the regeneration and recovery of the brachial plexus, and effectively slow down the decrease of Na+, K+-ATPase activities induced by the nerve injury, preventing muscular atrophy, and it promotes the generation of submandibular gland NGF, providing a favorable environment for regeneration of nerve"
We are continually adding more information on research and uses. Subscribe below to have us email them to you "hot off the press".

Several years ago Dr Graeme, a Chiropractor practicing in Victoria, Australia was looking for a serious hand held massager his patients could use at home to get the extra quality massage they needed. The ones he found in the shops and on-line for home use looked nice but were not serious, and... read more
Those experienced with courses of trigger point therapy such as dry needling, manual therapies and laser will understand that any relief... Read Article
As practitioners we are continually dealing with dysfunctional musculoskeletal systems. Typically dysfunction develops and is perpetuated... Read Article
Do not refresh or leave this page until loading complete.